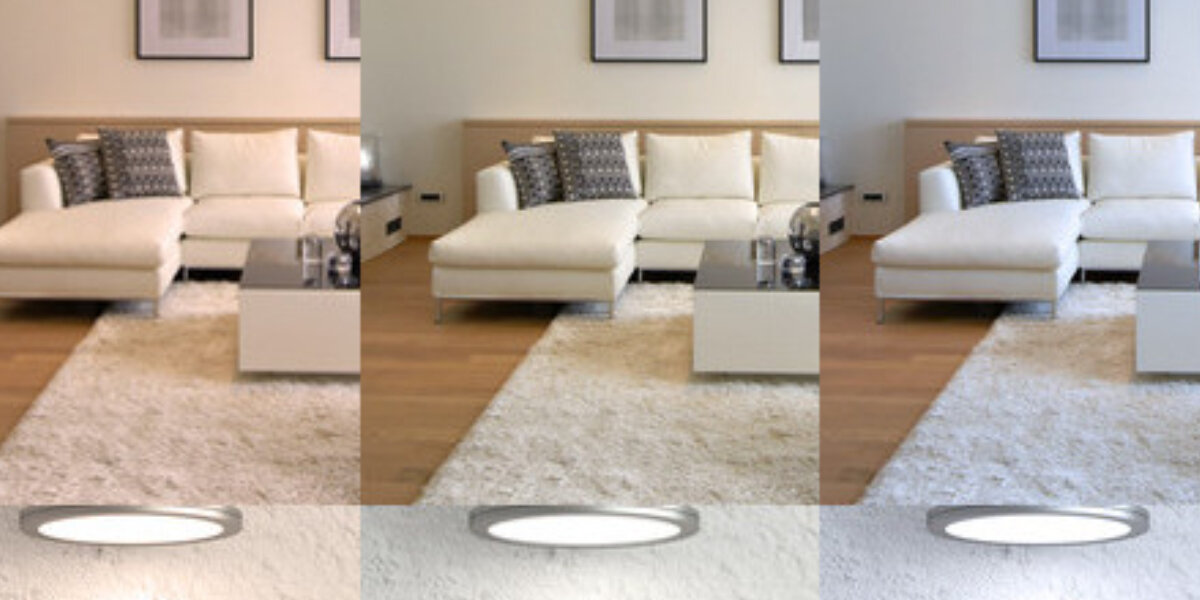
The Kelvin number is an important factor when buying a lamp. But what does this figure mean and which light colour is suitable for which requirement?
What does Kelvin mean for lamps?
The unit Kelvin indicates the colour temperature of a lamp. The Kelvin value of a lamp indicates whether the lamp emits warm light or cool light. A light with a low Kelvin number emits warm white light. The higher the Kelvin value, the cooler the lighting effect.
Kelvin" is named after William Thomson. The British physicist introduced and established the thermodynamic temperature scale "Kelvin" at the age of 24. To this day, people take the colour temperature in Kelvin into account for the lighting design of buildings, properties and commercial spaces.
Where can I find the information on the light colour?
Information on light colour can usually be found on the packaging of the respective light. The light temperature of a luminaire should also be taken into account as part of the lighting design.
What colour temperature is pleasant?
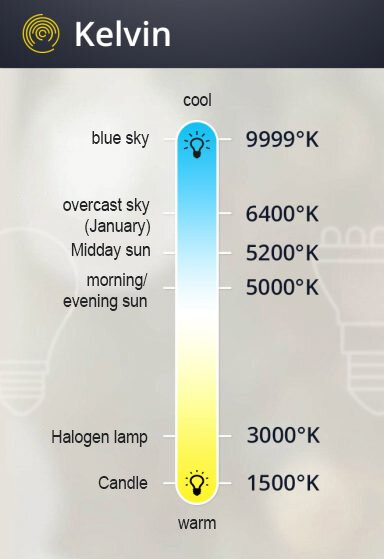
We perceive warm white light as cosy and comfortable; its colour temperature ranges up to 3,300 Kelvin. If the colour temperature of LEDs, xenon lamps and co. is below 3,300 Kelvin, the light is reminiscent of a sunset and is suitable for living rooms and bedrooms with this unobtrusive light.
Neutral white light activates and is therefore suitable for working in the hobby room or office. Light between 3,300 and 5,300 Kelvin has a sober but inviting effect. It is also the ideal light for make-up. The upper limit for neutral white light is 5,300 Kelvin. Up to this value, the light temperature of a luminaire is called neutral white.
Above this is the range of daylight white light that promotes concentration and is suitable, for example, for bright factory hall and shop lighting. Office lights should also emit daylight white light. Ranges of 7,000 to 10,000 Kelvin are ideal for bright outdoor lighting.
In relation to the various living spaces, the following guide values provide orientation:
|
Colour temperature in Kelvin |
|
|
Warm Light (<3,300 Kelvin, high red component) |
Cosy and comfortable |
|
Neutral white light (3,300 to 5,300 Kelvin) |
Stimulating |
|
Daylight white light (>5,300 Kelvin, high blue component) |
Increases concentration and performance |
|
Colour temperature in Kelvin |
|
|
Colour temperature for living room, bedroom |
2,700 Kelvin |
|
Colour temperature for kitchen, bathroom |
3,000 Kelvin |
|
Colour temperature for offices |
4,000 Kelvin |
| Industrial colour temperature | 6,500 Kelvin |
| Colour temperature for specialists like architects and photographers | 8,000 Kelvin |
Kelvin: Light and its Physical Principles
A term often used to describe the colour of light is "lighting mood". Cosy light, homely light, neutral light - this is how you create this individual lighting mood. But how many Kelvin should a light have to meet the respective requirements? There is only one way to find out: you have to measure the colour temperature. But how do you do that?
How you can imagine the colour temperature measurement
White light consists of many different frequency ranges in the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum. Light with a high red component appears warmer and darker, whereas light with a high blue component appears cooler and brighter. It is possible to precisely determine the colour temperature in Kelvin with a so-called colourimeter. To do this, the device performs a spectral analysis in which the light is broken down into different ranges. Each range has a different light intensity, which the colourimeter displays.
Colour measurements are not only possible with visible light, but can also be carried out for ultraviolet light and infrared light. With a colourimeter you can also test, for example, whether your screen is set too dark or too bright
How you can imagine the colour temperature measurement
At rising temperatures, solid materials eventually start to glow: for example, a grey iron turns into a luminous red material. The basis for measuring the colour temperature or light temperature is an ideal black body (which only exists in theory) that absorbs all incident light. If you heat it up, at some point it starts to emit red light, which becomes whiter and whiter and finally light blue as the temperature continues to rise via yellow hues. The colour temperature of a lamp figuratively indicates how hot the black body must be in order to emit light of the same colour.
Kelvin-Celsius conversion:
The unit kelvin also quite generally denotes the thermodynamic temperature worldwide. In Germany, the Celsius scale is more common: our reference value of 0 degrees Celsius corresponds to the value of 273.15 degrees on the Kelvin scale. Attention: The colour temperature of light is not, however, an indication of the temperature of the light shine, but refers to the outlined thought experiment with the "black body". The colour temperature describes the colour of light or the colour impression that characterises a light shine.
Scientific definition: The colour temperature of a light source corresponds to the temperature of a Plankian radiator (black body) at which it emits light in the same colour.
Colour rendering index: How good is the colour rendering of the lamp?
The same Kelvin values of a light source can correspond to completely different spectral compositions: Different lamps of the same light colour can therefore reproduce the colours of their surroundings differently in terms of realism (colour rendering index). This is particularly significant with LED lamps: cheap products in particular often have only a very limited spectrum of wavelengths of visible light; their light can be perceived as unpleasant. The light of incandescent lamps, on the other hand, is composed of almost all wavelengths of visible light, with yellow and red components predominating.








